Why Bees Are So Important And What Threats Are Bees Facing Today?
Bees, with their diligent pollination efforts, play a crucial role in our ecosystem and have a direct impact on human life. However, bees are currently facing significant threats that have far-reaching consequences for humans and the environment. In this blog post, we will explore the challenges bees are encountering in today’s world and delve into the consequences these threats pose to our well-being. It is essential to understand the gravity of the situation and take action to protect these invaluable pollinators.
What Role Do Bees Play in Our Lives?
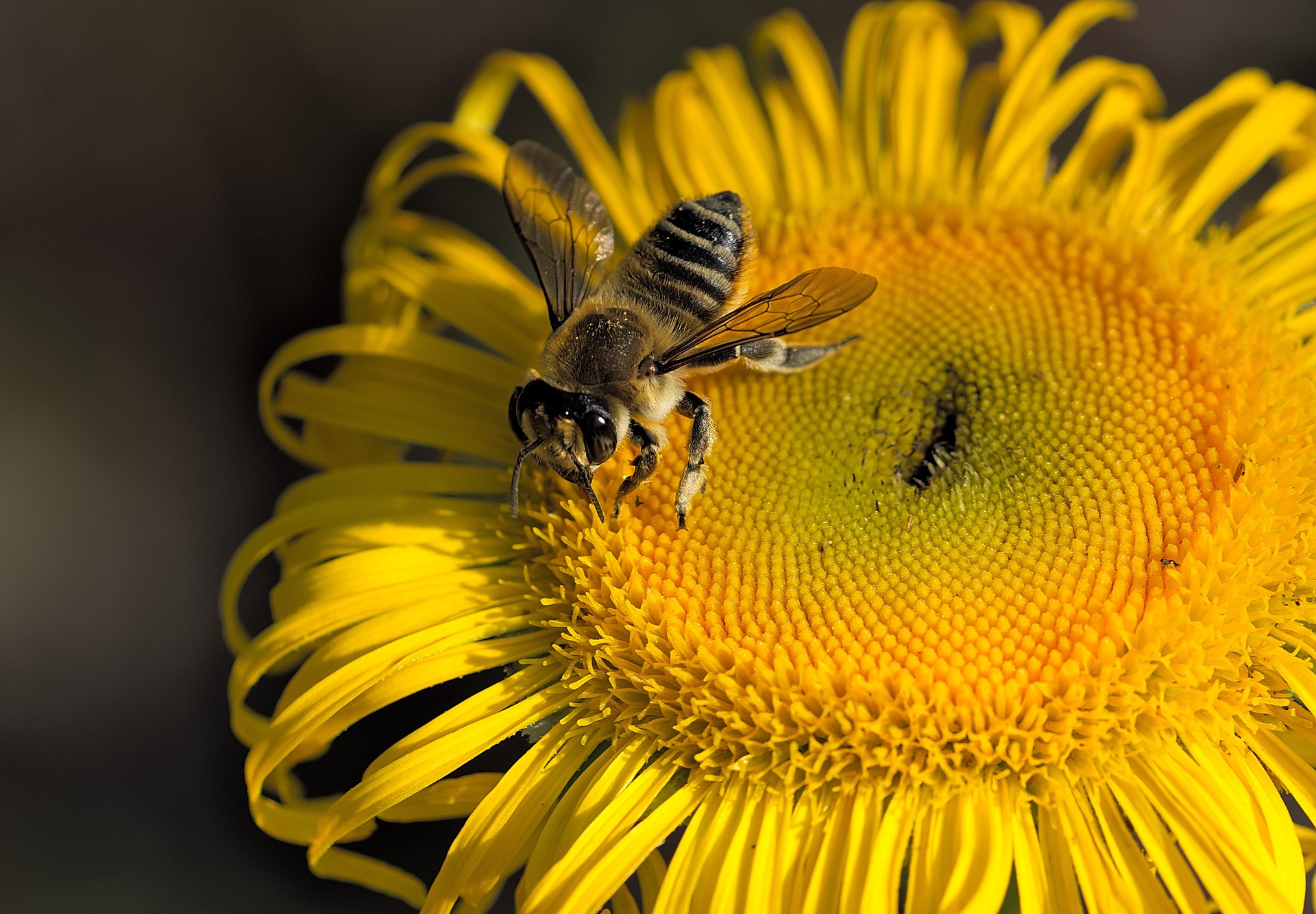
Bees are more than just buzzing insects; they are essential pollinators that contribute to the reproduction of many plant species. Approximately one-third of the global food supply relies on pollinators like bees. Without their assistance, the production of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds would be severely compromised. Bees facilitate the cross-pollination process by transferring pollen grains from the male parts of flowers to the female parts, allowing plants to reproduce and bear fruit. Their efforts lead to diverse and abundant harvests, ensuring food security for humans.
What Are the Most Serious Threats to Bees?
- Habitat Loss: The loss of natural habitats is a significant threat to bee populations. Urbanization, deforestation, and intensive agriculture have resulted in the destruction and fragmentation of their habitats. Bees require diverse and abundant food sources and suitable nesting sites to thrive. The loss of these habitats deprives bees of their essential resources and disrupts their life cycles.
- Pesticide Use: Pesticides, particularly neonicotinoids, have detrimental effects on bees. These chemicals are used in agriculture to protect crops from pests but inadvertently harm beneficial insects like bees. Pesticides can contaminate pollen and nectar, affecting bee health and behavior. They impair bees’ navigation and foraging abilities, making it difficult for them to find their way back to their hives.
- Climate Change: The changing climate poses challenges to bee populations. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt the synchronization between plants and their pollinators. Bees depend on the timing of flowering plants for their foraging activities. Climate change can cause mismatches between flowering periods and bee emergence, leading to a reduced availability of food resources.
- Diseases and Parasites: Bees face various diseases and parasites, including Varroa mites and viruses. These pathogens weaken bees’ immune systems and can cause colony collapse disorder, a phenomenon in which entire bee colonies rapidly decline and die. Disease outbreaks and infestations can devastate bee populations, further exacerbating their decline.
- Food Security: The decline of bee populations poses a significant threat to global food security. Many crops, including almonds, apples, blueberries, and melons, heavily rely on bee pollination for successful fruit set and quality. Without adequate pollination, crop yields would decrease, leading to lower production and increased food prices. The loss of bee pollinators could result in shortages of essential food items, impacting both our diets and economies.
- Biodiversity Loss: Bees are not only essential for food production but also for maintaining biodiversity. As pollinators, they contribute to the reproduction and survival of numerous plant species. The decline in bee populations can disrupt entire ecosystems, leading to a loss of plant diversity and negatively affecting other animals that depend on those plants. The intricate web of interactions within ecosystems can unravel without the crucial services provided by bees.
- Economic Impact: Bees’ role in pollination extends beyond food production; it also has substantial economic implications. The agricultural and horticultural industries heavily rely on bee pollination services. Diminished bee populations can result in increased costs for farmers, reduced agricultural productivity, and job losses within these sectors. The economic ripple effects can be felt throughout the supply chain, impacting industries and consumers alike.
- Environmental Balance: Bees play a vital role in maintaining the balance of our environment. Their pollination activities contribute to the growth of forests, meadows, and other natural habitats. Without bees, these ecosystems would suffer, leading to a decline in air quality, water filtration, and overall environmental health. The loss of bees can disrupt the intricate relationships between plants, animals, and their surroundings, leading to imbalances and potential ecosystem collapse.
What Actions Must Be Taken To Protect Bees?
To address the threats faced by bees and mitigate their consequences, collective action is crucial. Here are some steps we can take:
- Protect and Restore Habitat: Support initiatives that aim to protect and restore bee habitats. Plant native, bee-friendly flowers and create green spaces in our communities that provide food and nesting sites for bees.
- Use Pesticides Responsibly: Opt for organic and pesticide-free alternatives in our gardens and encourage responsible pesticide use in agriculture. Support practices that prioritize integrated pest management and minimize harm to beneficial insects like bees.
- Support Local Beekeepers: Purchase honey and other bee-related products from local beekeepers who follow sustainable and bee-friendly practices. Supporting these beekeepers encourages responsible beekeeping and helps maintain local bee populations.
- Spread Awareness: Educate others about the importance of bees and the threats they face. Promote sustainable gardening practices, such as planting bee-friendly flowers, minimizing pesticide use, and providing water sources for bees. Advocate for policies that protect bee populations and promote habitat conservation.
Conclusion
The threats faced by bees today are cause for concern, given their vital role in our ecosystems and their significant impact on human life. The consequences of declining bee populations range from food security challenges to biodiversity loss, economic impacts, and imbalances in our environment. By recognizing the importance of bees and taking action to protect them, we safeguard our own future and that of the planet. Let us collectively work towards preserving bee populations, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering a harmonious coexistence with these essential pollinators. Together, we can make a difference and secure a thriving future for bees and humanity.